The transformative world of Generative AI (GenAI), which refers to artificial intelligence systems capable of creating new content such as text, images, or music that is similar to human-generated content, has become integral to innovation, powering the next generation of AI-enabled applications. At Grab, it is crucial that every Grabber has access to these cutting-edge technologies to build powerful applications to better serve our customers and enhance their experiences. Grab’s AI Gateway aims to provide exactly this. The gateway seamlessly integrates AI providers like OpenAI, Azure, AWS (Bedrock), Google (VertexAI) and many other AI models, to bring seamless access to advanced AI technologies to every Grabber.
Why do we need Grab AI Gateway?
Before we begin implementing Grab AI Gateway in our work process, it is important for us to understand the limitations as well as the solutions that Grab AI Gateway provides. Failure to properly implement Grab AI Gateway could lead to roadblocks in development which negatively affect user experience.
Streamline access
Each AI provider has its own way of authenticating their services. Some providers use key-based authentication while others require instance roles or cloud credentials. Grab AI Gateway provides a centralised platform that only requires a one-time provider access setup. Grab AI Gateway removes the effort of procuring resources and setting up infrastructure for AI services, such as servers, storage, and other necessary components.
Enables experimentation
By providing a simple unified way to access different AI providers, users can experiment with various Large Language Models (LLMs) and choose the one best suited for their task.
Cost-efficient usage
Many AI providers allow purchasing of reserved capacity to provide higher throughput and improve cost effectiveness. However, services that require reservation or pre-purchases over a commitment period can lead to wastage.
Grab AI Gateway overcomes this problem and minimises wastage with a shared capacity pool. A deprecated service would simply free up bandwidth for a new service to utilise. Additionally, Grab AI Gateway provides a global view of usage trends to help platform teams make informed decisions on reallocating reserved capacity according to demand and future trends (eg. an upcoming model replacing an old one).
Auditing
A central setup ensures that use cases undergo a thorough review process to comply with the privacy and cyber security standards before being deployed in production. For instance, a Q&A bot with access to both restricted and non-restricted data could inadvertently reveal sensitive information if authorisation is not set up properly. Therefore, it is important that use cases are reviewed to ensure they follow Grab’s standard for data privacy and protection.
Platformisation benefits
Proper implementation of a central gateway provides platformisation benefits like:
- Reduced operational costs.
- Centralised monitoring and alerts.
- Cost attribution.
- Control limits like maximum QPS and cost cap.
- Enforce guardrail and safety from prompt injection.
Architecture and design
At its core, the AI Gateway is a set of reverse proxies to different external AI providers like Azure, OpenAI, AWS, and others. From the user’s perspective, the AI Gateway acts like the actual provider where users are only required to set the correct base URLs to access the LLMs. The gateway handles functionalities like authentication, authorisation, and rate limiting, allowing users to solely focus on building GenAI enabled applications.
To form the basis of identity and access management (IAM) in the gateway, API key can be requested by the user for exploration (short-term personal key) or production (long-term service key) usage. The gateway implements a request path based authorisation where certain keys can be granted access to specific providers or features. Once authenticated, the AI Gateway replaces the internal key in request with the provider key and executes the request on behalf of the user.
The AI Gateway is designed with a minimalist approach, often serving as a lightweight interface between the user and the provider, intervening only when necessary. This has enabled us to keep up with the pace of innovation in the field and to continue expanding the provider catalogue without increasing the ops burden. Similar to requests, responses from the provider are returned to the user with no to minimal processing time. The gateway is not limited to only chat completion API. It exposes other APIs like embedding, image generation, and audio along with functionalities like fine-tuning, file storage, search, and context caching. The gateway also provides access to in-house open source models. This provides a taste of open source software (OSS) capabilities that users can later decide to deploy a dedicated instance using Catwalk’s VLLM offering.
User journey and features
Onboarding process
GenAI based applications come with inherent risks like generating offensive or incorrect output and hostile takeover by malicious actors. As software practices and security standards for building GenAI applications are still evolving, it is important for users to be aware of the potential pitfalls. As AI Gateway is the de facto way to access this technology, the platform team shares the responsibility of building such awareness and ensuring compliance. The onboarding process includes a manual review stage. Every new use case requires a mini-RFC (Request For Comments) and a checklist that is reviewed by the platform team. In certain cases, an in-depth review by the AI Governance task force may be requested. To reduce friction, users are encouraged to build prototypes and experiment with APIs using “exploration keys”.
Exploration keys
At Grab, every Grabber is encouraged to use GenAI technologies to improve productivity and to experiment and learn within this field. The gateway provides exploration keys to make it easier for users to experiment with building chatbots and Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG). These keys can be requested by Grabbers through a Slack bot. The keys are short-lived with a validity period of a few days, stricter rate limit restrictions, and access limited to only the staging environment. Exploration keys are highly popular, with more than 3,000 Grabbers requesting the key to experiment with APIs.
Unified API interface
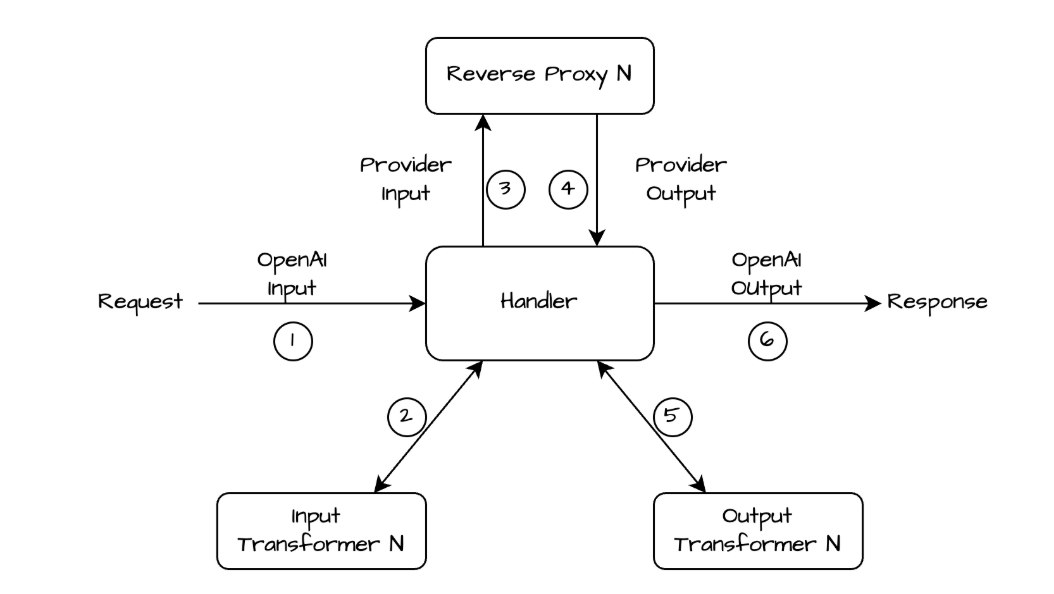
In addition to provider specific interface, the gateway also offers a single interface to interact with multiple AI providers. For users, this lowers the barrier of experimenting between different providers/models, as they do not need to learn and rewrite their logic for different SDKs. Providers can be switched simply by changing the “model” parameter in the API request. This also enables easy setup of fallback logic and dynamic routing across providers. Based on popularity, the gateway uses the OpenAI API scheme to provide the unified interface experience. The API handler translates the request payload to the provider specific input scheme. The translated payload is then sent to reverse proxies. The returned response is translated back to the OpenAI response scheme.
Dynamic routing
The AI Gateway plays a crucial role in maintaining usage efficiency of various reserved instance capacities. It provides the control points to dynamically route requests for certain models to a different albeit similar model backed by a reserved instance. Another frequent use case is smart load balancing across different regions to address region-specific constraints related to maximum available quotas. This approach has helped to minimise rate limiting.
Auditing
The AI Gateway records each call’s request, response body, and additional metadata like token usage, URL path, and model name into Grab’s data lake. The purpose of doing so is to maintain a trail of usage which can be used for auditing. The archived data can be inspected for security threats like prompt injection or potential data policy violations.
Cost attribution
Allocating costs to each use case is important to encourage responsible usage. The cost of calling LLMs tends to increase at higher request rates, therefore understanding the incurred cost is crucial to understanding the feasibility of a use case. The gateway performs cost calculations for each request once the response is received from the provider. The cost is archived in the data lake along with an audit trail. For async usages like fine-tuning and assisting, the cost is calculated through a separate daily job. Finally, a job aggregates the cost for each service which is used for reporting on dashboards and showback. In addition, alerts are configured to notify if a service exceeds the cost threshold.
Rate limits
AI Gateway enforces its own rate limit on top of the global provider limits to make sure quotas are not consumed by a single service. Currently, limits are enforced on the request rate at the key level.
Integration with the ML Platform
At Grab, the ML platform serves as a one-stop shop, facilitating each phase of the model development lifecycle. The AI Gateway is well integrated with systems like Chimera notebooks used for ideation/development to Catwalk for deployment. When a user spins up a Chimera notebook, an exploration key is automatically mounted and is ready for use. For model deployments, users can configure the gateway integration which sets up the required environment variables and mounts the key into the app.
Challenges faced
With more than 300 unique use cases onboarded and many of those making it to production, AI Gateway has gained popularity since its inception in 2023. The gateway has come a long way, with many refinements made to the UX and provider offerings. The journey has not been without its challenges. Some of the challenges have become more prominent as the number of apps deployed increases.
Keeping up with innovations
With new features or LLMs being released at a rapid pace, the AI Gateway development has required continuous dedicated effort. Reflecting on our experience, it is easy to get overwhelmed by a constant stream of user requests for each new development in the field. However, we have come to realise it is important to balance release timelines and user expectations.
Fair distribution of quota
Every use case has a different service level objective (SLO). Batch use cases require high throughput but can tolerate failures while online applications are sensitive to latency and rate limits. In many cases, the underlying provider resource is the same. The responsibility falls over to the gateway to ensure fair distribution based on criticality and requests per second (RPS) requirements. As adoption increases, we have encountered issues where batch usage interfered with the uptime of online services. The use of Async APIs does mitigate the issues, but not all use cases can adhere to turnaround time.
Maintaining reverse proxies
Building the gateway as a reverse proxy was a key design decision. While the decision has proven to be beneficial, it is not without its complexity. The design ensures that the gateway is compatible with provider-specific SDKs. However, over time, we have encountered edge cases where certain SDK functionalities do not work as expected due to a missing path in the gateway or a missing configuration. These issues are usually ironed out when caught and a suite of integration tests with SDKs are conducted to ensure there are no breaking changes before deploying.
Current use cases and applications
Today, the gateway powers many AI-enabled applications. Some examples include real time audio signal analysis for enhancing ride safety, content moderation to block unsafe content, and description generator for menu items and many others.
Internally, the gateway powers innovative solutions to boost productivity and reduce toil. A few examples are:
- GenAI portal that is used for translation and language detection tasks, image generation, and file analysis.
- Text-to-Insights for converting questions into SQL queries.
- Incident management automation for triaging incidents and creating reports.
- Support bot for answering user queries in Slack channels using a knowledge base.
What’s next?
As we continue to add more features, we plan to focus our efforts on these areas:
1. Catalogue
With over 50 AI models each suited for a specific task type, finding the correct model to use is becoming complex. Users are often unsure of the difference between models in terms of capabilities, latency, and cost implications. A catalogue can serve as a guideline by listing currently supported models along with the list of metadata like the input/output modality, token limits, provider quota, pricing, and reference guide.
2. Out of box governance
Currently, all AI-enabled services that process clear text input and output from customers require users to set up their own guardrails and safety measures. By creating a built-in support for security threats like prompt injection and guardrails for filtering input/output, we can save users significant effort.
3. Smarter rate limits
At the current time, the gateway supports basic request rate-based limits at key level. While this rudimentary offering has been proven useful, it has its limitations. More advanced rate limiting policies based on token usage or daily/monthly running costs should be introduced to enforce better and fairer limits. These policies can be modified to be applied on different models and providers.
Special thanks to Priscilla Lee, Isella Lim, and Kevin Littlejohn for helping us in the project and Padarn Wilson for his leadership.
Grab is the leading superapp platform in Southeast Asia, providing everyday services that matter to consumers. More than just a ride-hailing and food delivery app, Grab offers a wide range of on-demand services in the region, including mobility, food, package and grocery delivery services, mobile payments, and financial services across 700 cities in eight countries.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!