The European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA) has published the final report and a standalone executive summary of the Machine Learning Application Approval (MLEAP) project.
The report was developed by the project consortium consisting of Airbus protect, LNE (Laboratoire National de Métrologie et d’Essais), and Numalis, following a 2-year Research Project funded by Horizon Europe. The European Commission delegated the contractual and technical management of this research action to EASA.
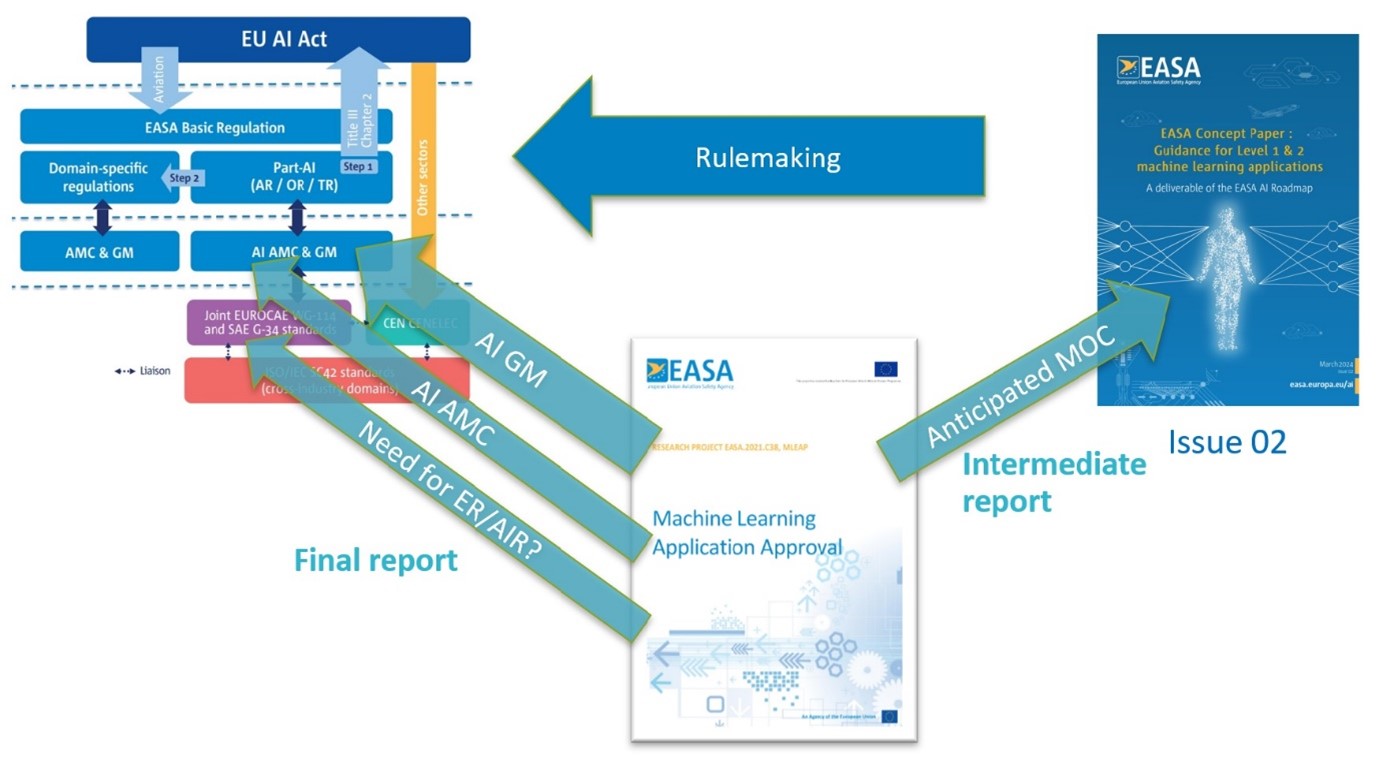
The MLEAP Research Project supports the EASA Artificial Intelligence (AI) Programme and is aimed at identifying concrete means of compliance for the ‘Learning Assurance’ block of the EASA AI Concept Paper Issue 2.
Three main technical axes were investigated during the Project:
- data representativeness;
- generalisation guarantee; and
- model and learning algorithm robustness and guarantee.
After a deep dive in the state of the art and following the evaluation of complex aviation use cases, some methods and tools were identified and assessed. A generic development pipeline was proposed by the consortium as a practical implementation of the EASA W-shape development process.
The first findings from the MLEAP Project have been used to enrich the EASA AI Concept Paper Issue 2. Furthermore, the final report findings will provide crucial support for EASA’s AI Rulemaking Task RMT.0742 and EASA’s involvement in EUROCAE Working Group WG-114.
On 3 July 2024, during the EASA AI Days, the MLEAP consortium will present detailed results of the Project and address any queries. Registration for this event is still open via the EASA Artificial Intelligence Days — High-Level Conference 2024 page.



