Introduction
At the recent COP16 conference in Cali, Colombia, the Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD) announced that over 500 organizations have committed to aligning their risk management and corporate reporting practices with its recommendations. This represents a remarkable 57% increase in adoption since January 2024, underscoring a growing recognition of the importance of nature-related risks in financial decision-making.
Key Highlights
1. Scope of Adoption
A total of 502 firms and financial institutions from 54 jurisdictions and 62 sectors are now integrating the TNFD framework into their operations. This includes 129 financial institutions collectively managing approximately $17.7 trillion in assets. The broad participation across various sectors demonstrates a concerted effort to incorporate nature-related financial risks into corporate strategies and reporting.
2. Global Reach and Impact
The TNFD framework aims to provide organizations with a structured approach to identify, assess, and disclose nature-related risks. By adopting this framework, companies can enhance their resilience to environmental challenges, thereby contributing to sustainable development goals. As highlighted by the TNFD, this commitment aligns closely with international efforts to mitigate biodiversity loss and combat climate change.
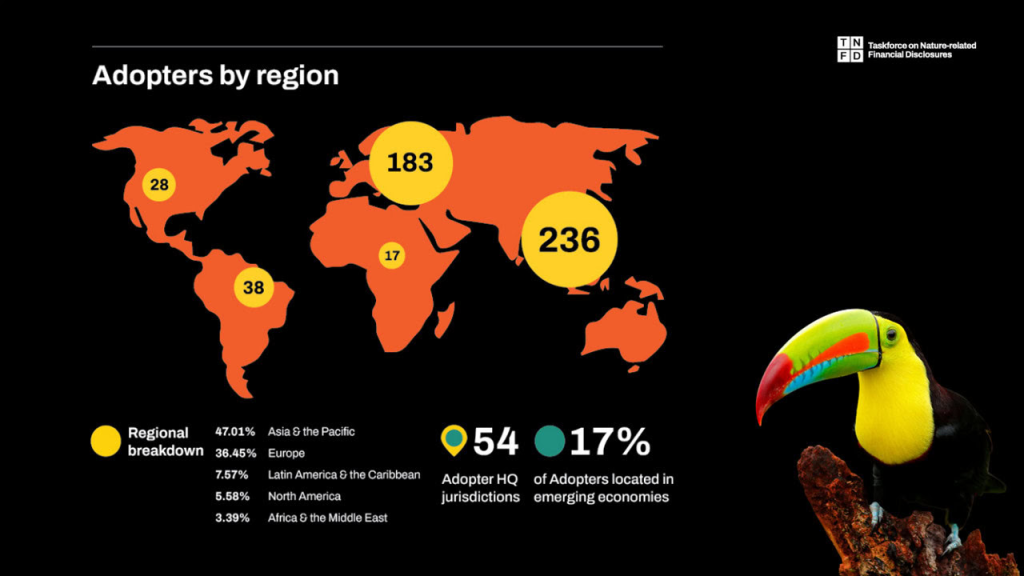
3. Alignment with Global Goals
The TNFD framework operationalizes Target 15 of the Global Biodiversity Framework, which encourages corporate transparency regarding nature-related risks. This alignment is critical as it fosters greater accountability among businesses, allowing stakeholders to understand how their activities impact ecosystems. The framework not only promotes better risk management but also aids in informing investment decisions, supporting a transition to a more sustainable economy.
The Significance of Nature-Related Risk Management
1. Understanding Nature-Related Risks
Nature-related risks encompass a range of issues, including biodiversity loss, deforestation, and water scarcity. According to the World Economic Forum, these risks can have significant financial implications for businesses. For instance, the degradation of ecosystems can disrupt supply chains, increase operational costs, and result in regulatory fines.
2. Corporate Responsibility and Transparency
As stakeholder expectations evolve, there is a growing demand for transparency in corporate sustainability efforts. A report from PwC indicates that 79% of investors are concerned about how companies are managing environmental risks. By adopting the TNFD framework, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to environmental stewardship and accountability, enhancing their reputation and investor confidence.
3. Financial Institutions Leading the Charge
The adoption of the TNFD framework is particularly notable among financial institutions, which play a crucial role in driving sustainable finance. With over $17 trillion in assets under management, these institutions have the potential to influence corporate behavior significantly. By integrating nature-related risk assessments into their investment processes, they can promote sustainable practices across industries.
Conclusion
The recent announcement by the TNFD marks a pivotal moment in the integration of nature-related risk management into corporate and financial reporting. With over 500 firms, including major financial institutions, committing to this framework, the momentum for sustainable business practices is growing. As organizations align their strategies with global biodiversity goals, the adoption of the TNFD framework not only helps mitigate risks but also fosters a more sustainable and resilient future for both businesses and the planet.
References
- Taskforce on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD). (2024). Announcement at COP16.
- World Economic Forum. (2022). The Global Risks Report.
- PwC. (2023). The Investor Agenda: Climate Action.
- Convention on Biological Diversity. (2022). Global Biodiversity Framework.

