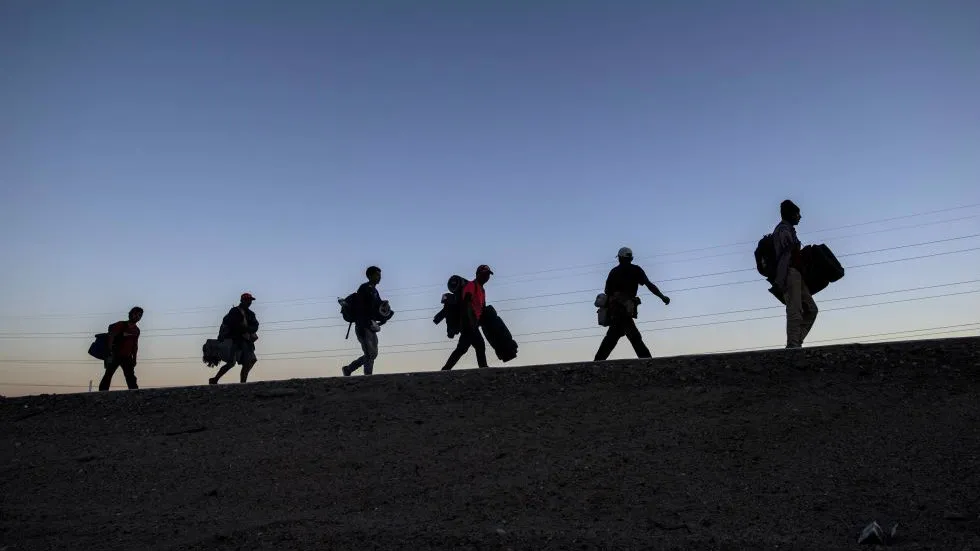
Introduction
The European Union (EU) faces a complex dilemma when it comes to immigration. While many EU countries are experiencing labor shortages and declining birth rates, leading to a pressing need for workers, there is a notable resistance to immigration in several member states. This paradox raises questions about the EU’s immigration policies, public sentiment, and the broader implications for the future of Europe’s workforce.
The Labor Market Needs
1. Aging Population
Many EU countries, particularly in Southern and Eastern Europe, are grappling with an aging population. With a declining birth rate, there are fewer young people entering the workforce, leading to significant gaps in various sectors. Industries such as healthcare, construction, and technology urgently require skilled workers to sustain economic growth and public services.
2. Labor Shortages
Several EU countries are currently experiencing labor shortages, with many sectors unable to fill vacancies. For instance, hospitality and agriculture frequently rely on migrant labor, particularly during peak seasons. The need for foreign workers is evident, yet the political climate often complicates the situation.
The Resistance to Immigration
1. Public Sentiment and Political Landscape
Despite economic needs, public sentiment in many EU countries tends to be wary of immigration. Concerns about integration, cultural differences, and social cohesion often dominate discussions. Right-wing political parties have capitalized on these fears, framing immigration as a threat to national identity and security, which influences public policy.
2. Security Concerns
Issues related to security and terrorism have also fueled resistance to immigration. High-profile incidents linked to migrants can lead to increased scrutiny and skepticism towards all immigrants, overshadowing the economic benefits they might bring. The fear of not being able to adequately vet newcomers often results in stricter immigration controls.
3. EU Policy and Fragmentation
The EU itself has faced challenges in creating a cohesive immigration policy. Disagreements among member states regarding responsibility for asylum seekers and migrants have led to a fragmented approach. Some countries, particularly those on the frontlines of migration, feel overwhelmed, while others resist taking in migrants altogether.
4. Economic Anxiety
Economic instability in some regions can exacerbate resistance to immigration. Citizens may feel that incoming migrants compete for jobs, driving wages down and increasing unemployment. This anxiety can lead to protectionist attitudes, even in countries that ultimately need more workers.
The Path Forward
1. Balancing Labor Needs with Integration
For the EU to address its labor shortages effectively, there must be a balanced approach that promotes both immigration and integration. This includes developing pathways for skilled workers to enter the EU, along with support systems to facilitate their integration into society.
2. Public Education Campaigns
Educating the public about the economic benefits of immigration can help shift attitudes. Highlighting success stories and the contributions of immigrants to local economies can foster a more positive perception.
3. Revising Immigration Policies
The EU may need to revisit its immigration policies to make them more flexible and responsive to labor market needs. Streamlined processes for skilled migrants, seasonal workers, and refugees could help fill gaps while maintaining humanitarian commitments.
Conclusion
The EU’s resistance to immigration amidst labor shortages presents a complex challenge. Balancing economic needs with public sentiment and security concerns is no easy task. However, recognizing the potential benefits of immigration and creating a cohesive strategy that addresses both labor needs and integration can pave the way for a more prosperous and inclusive Europe. As the demographics of Europe continue to shift, finding solutions that embrace migration as a vital part of economic growth will be crucial for the continent’s future.