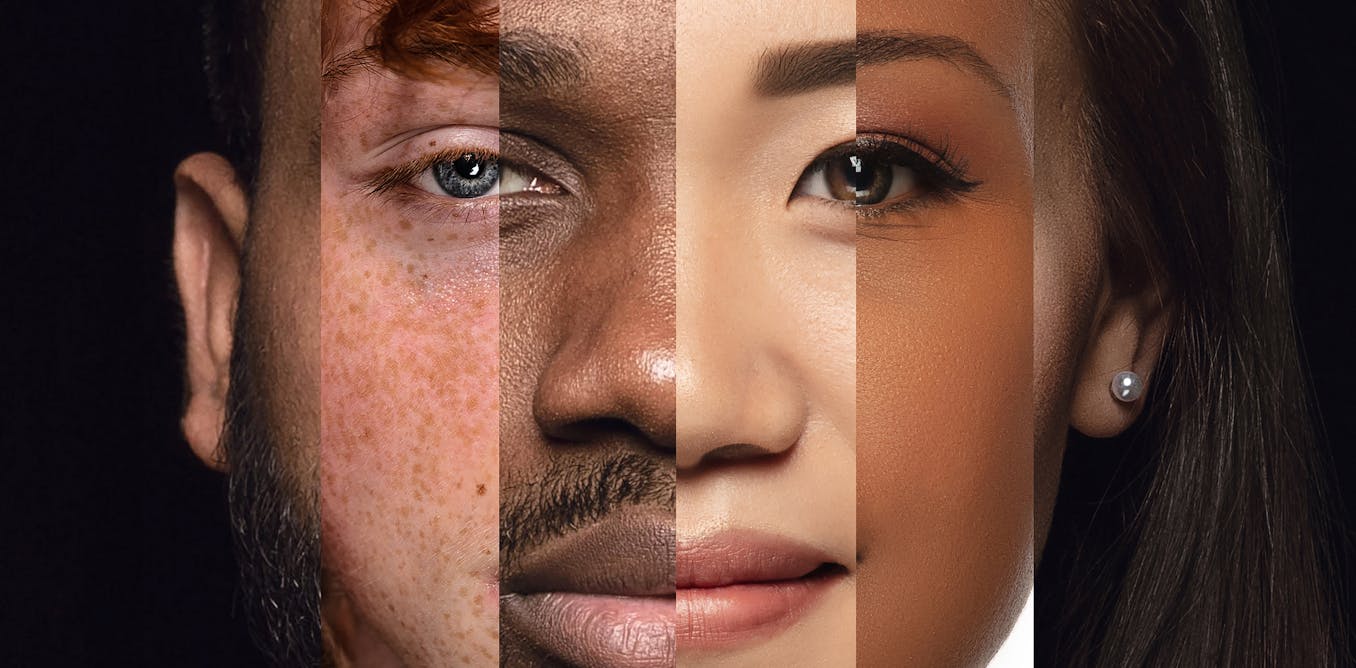
The more gender equal a society is, the more similar men and women will be, adopting more similar interests, personality traits and behavioural patterns. Or so many people seem to believe.
Statements like this might sound like truisms, but science shows reality may be more complicated.
Several studies have found that some psychological sex differences, such as those in personality, are larger in more gender-equal countries. The same goes for countries that are more educated, prosperous and otherwise have better living conditions. This has become known as the gender-equality paradox.
Until recently, it was unclear how widespread this pattern might be. My team, which included research assistant Kare Hedebrant, tried to address that in a recently published study, where we investigated which psychological sex differences are associated with living conditions and, if so, how.
The study covered a range of themes, from personality and cognitive functions to sexting and circadian rhythm. Our study focused on mostly western countries but used some data from other countries such as India and Kenya.
We reviewed 54 articles that analyse the relationship between magnitudes of psychological sex differences and country-level indicators of living conditions. We also used data from 27 meta-analyses (reviews of previous research) of psychological sex differences and conducted new analyses to determine associations between sex differences and national economy, education, health, gender equality and more.
Sex differences
Each study used data from at least five countries, usually spanning several decades.
We grouped the many psychological dimensions covered by these studies into six categories: personal characteristics, cognition, interpersonal relations, emotion, academic preferences (such as a pull towards science, technology, engineering and maths) and morals and values.
Our findings paint a complex picture, showing that variation in psychological sex difference did not follow a uniform pattern. In countries with better living conditions, males and females are more alike in some regards and more different in others.
For example, differences in personality characteristics were frequently found to be larger in countries with better living conditions. This includes traits such as extroversion, agreeableness and altruism, which research seems to show are more strongly associated with women. The same was true for sex differences in some dimensions of emotion, specifically negative emotions in which females tend to score higher, such as shame.
StunningArt/Shutterstock
There were also exceptions to the gender-equality paradox. Sex differences in sexual behaviour, like engaging in casual sex, were consistently found to be smaller in countries with better living conditions. This is probably because women in these countries, where there are more permissive norms, have better access to contraceptives.
A complicated phenomenon
For cognitive functions, sex differences were sometimes larger, sometimes smaller in countries with better living conditions. Interestingly, the sex differences were larger in cognitive domains where women have strengths.
For instance, episodic memory (memory for experienced events) and verbal ability, where females typically do better than males, saw larger sex differences as living conditions improved. Females got better at episodic memory when they had better living conditions. By contrast, sex differences in semantic memory (memory for facts) and mathematical ability, where males tend to do better, decreased when living conditions improved.
This suggests that, when it comes to cognitive abilities, females benefit more than males from improvements in living conditions. The performance gap increases in domains where females have an advantage and closes in domains where males are ahead.
Not all psychological sex differences were associated with living conditions in the same way. So, can we say that there is a gender-equality paradox? Yes, to some extent, since more sex differences grew, rather than decreased, in countries with better living conditions.
In most cases, however, psychological sex difference magnitudes were not significantly associated with living conditions. This suggests that, in general, psychological sex differences are not greatly affected by living conditions but seem instead quite stable. For instance, research often finds females get higher grades at school across different subjects. It’s also common for researcher to find males have greater interest in maths. But neither seems to be affected by living conditions.
Even in cases where the magnitude of sex differences did vary in relation to living conditions, the pattern of male and female advantages usually remained the same. So, for example, though the female advantage over males in episodic memory ability is greater in some countries than others, females outperform males in almost all countries.
In summary, we found little support for the idea that psychological sex differences will vanish as societies develop. Policymakers probably cannot rely on that if they hope to achieve equal distributions of men and women in different professions. Instead, it appears that the dominant feature of psychological sex differences is their robustness in the face of social change.