The advertising industry is constantly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and changes in consumer behaviour. One of the key challenges in this industry is reaching the right audience, reaching people who are most likely to be interested in your product or service. This is where the concept of a lookalike audience comes into play. By identifying and targeting individuals who share similar characteristics with an existing customer base, businesses can significantly improve the effectiveness of their advertising campaigns.
However, as the scale of Grab advertisements grows, there are several optimisations needed to maintain the efficacy of creating lookalike audiences such as high service level agreement (SLA), high cost of audience creation, and unstable data ingestion.
The need for an even more efficient and scalable solution for creating lookalike audiences was the motivation behind the development of the scalable lookalike audience platform. By developing a high-performance in-memory lookalike audience retrieval service and embedding-based lookalike audience creation and updating pipelines, this improved platform builds on the existing system and provides an even more effective tool for advertisers to reach their target audience.
Constant optimisation for greater precision
In the dynamic world of digital advertising, the ability to quickly and efficiently reach the right audience is paramount and a key strategy is targeted advertising. As such, we have to constantly find ways to improve our current approach to creating lookalike audiences that impacts both advertisers and users. Some of the gaps we identified included:
-
Long SLA for audience creation. Earlier, the platform stored results on Segmentation Platform (SegP) and it took two working days to generate a lookalike audience list. This is because inserting a single audience into SegP took three times longer than generating the audience. Extended creation times impacted the effectiveness of advertising campaigns, as it limited the ability of advertisers to respond quickly to changing market dynamics.
-
Low scalability. As the number of onboarded merchant-partners increased, the time and cost of generating lookalike audiences also increased proportionally. This limited the availability of lookalike audience generation for all advertisers, particularly those with large customer bases or rapidly changing audience profiles.
-
Low updating frequency of lookalike audiences. With automated updates only occurring on a weekly basis, this increased the likelihood that audiences may become outdated and ineffective. This meant there was scope to further improve to help advertisers more effectively reach their campaign goals, by targeting individuals who fit the desired audience profile.
-
High cost of creation. The cost of producing one segment can add up quickly for advertisers who need to generate multiple audiences. This could impact scalability for advertisers as they could hesitate to effectively use multiple lookalike audiences in their campaigns.
Solution
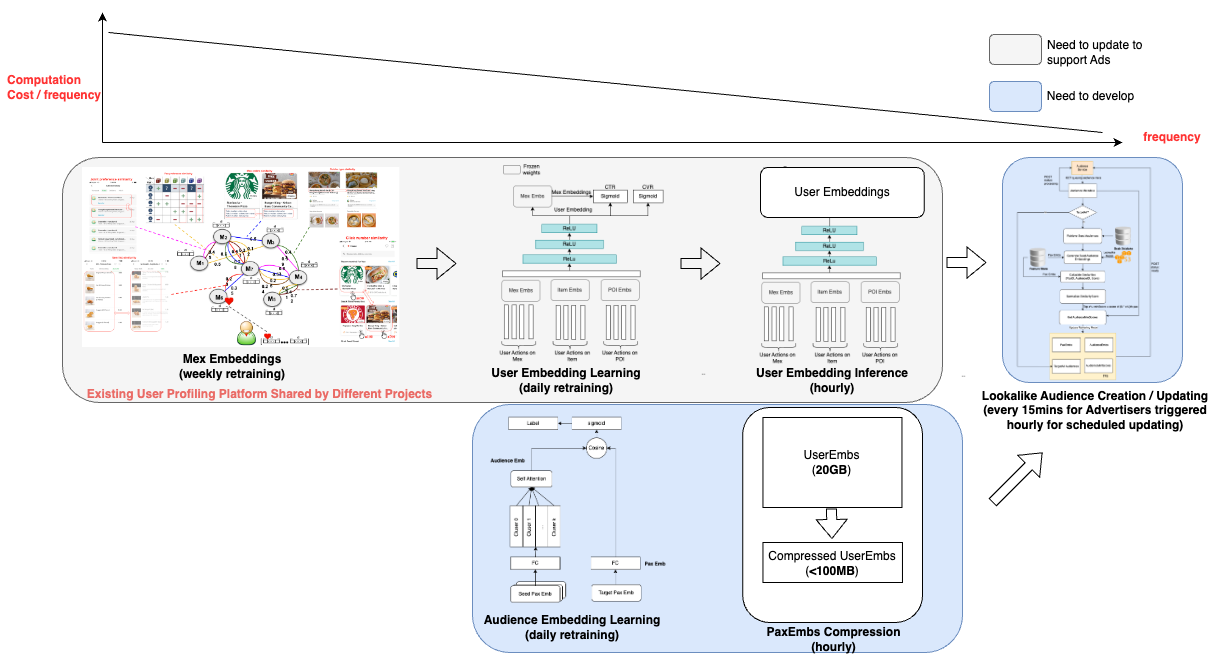
To efficiently identify the top N lookalike audiences for each Grab user from our pool of millions of users, we developed a solution that leverages user and audience representations in the form of embeddings. Embeddings are vector representations of data that utilise linear distances to capture structure from the original datasets. With embeddings, large sets of data are compressed and easily processed without affecting data integrity. This approach ensures high accuracy, low latency, and low cost in retrieving the most relevant audiences.
Our solution takes into account the fact that representation drift varies among entities as data is added. For instance, merchant-partner embeddings are more stable than passenger embeddings. By acknowledging this reality, we optimised our process to minimise cost while maintaining a desirable level of accuracy. Furthermore, we believe that having a strong representation learning strategy in the early stages reduced the need for complex models in the following stages.
Our solution comprises two main components:
-
Real-time lookalike audience retrieving: We developed an in-memory high-performance retrieving service that stores passenger embeddings, audience embeddings, and audience score thresholds. To further reduce cost, we designed a passenger embedding compression algorithm that reduces the memory needs of passenger embeddings by around 90%.
-
Embedding-based audience creation and updating: The output of this part of the project is an online retrieving model that includes passenger embeddings, audience embeddings, and thresholds. To minimise costs, we leverage the passenger embeddings that are also utilised by other projects within Grab, beyond advertising, thus sharing the cost. The audience embeddings and thresholds are produced with a low-cost small neural network.
In summary, our approach to creating scalable lookalike audiences is designed to be cost-effective, accurate, and efficient, leveraging the power of embeddings and smart computational strategies to deliver the best possible audiences for our advertisers.
Solution architecture
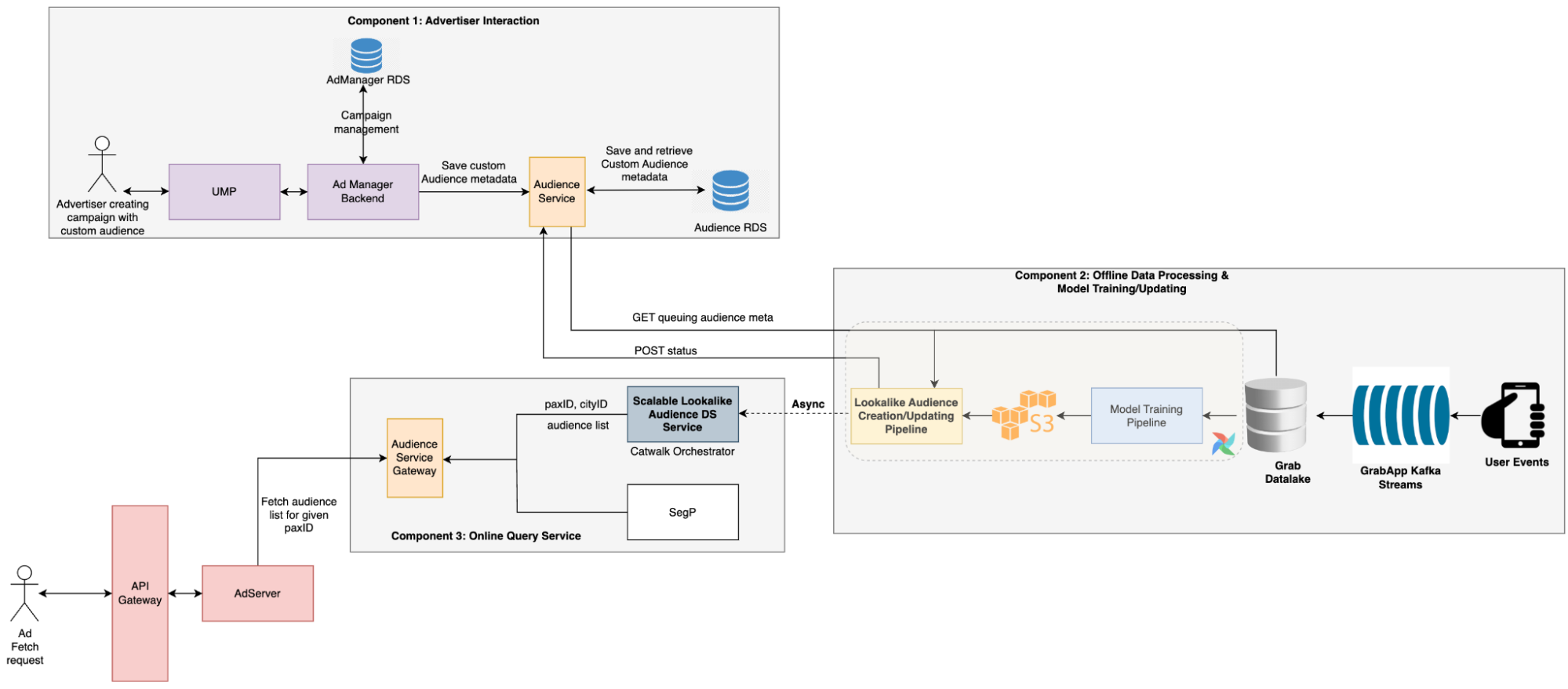
- The advertiser creates a campaign with a custom audience, which triggers the audience creation process. During this process, the audience service stores the audience metadata provided by advertisers in a message queue.
- A scheduled Data Science (DS) job then retrieves the pending audience metadata, creates the audience, and updates the TensorFlow Serving (TFS) model.
- During the serving period, the Backend (BE) service calls the DS service to retrieve all audiences that include the target user. Ads that are targeting these audiences are then selected by the Click-Through Rate (CTR) model to be displayed to the user.
Implementation
To ensure the efficiency of the lookalike audience retrieval model and minimise the costs associated with audience creation and serving, we’ve trained the user embedding model using billions of user actions. This extensive training allows us to employ straightforward methods for audience creation and serving, while still maintaining high levels of accuracy.
Creating lookalike audiences
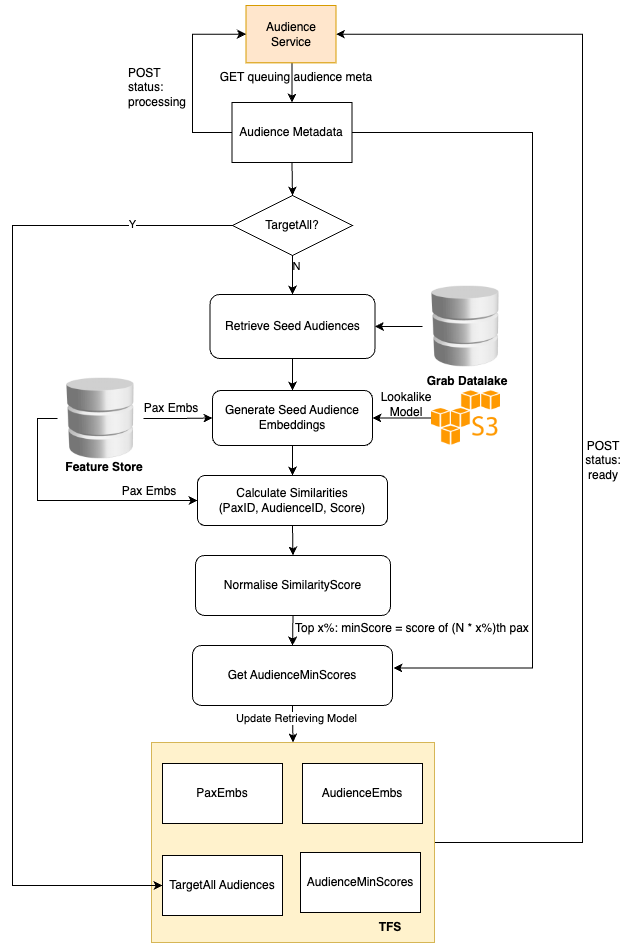
The Audience Creation Job retrieves the audience metadata from the online audience service, pulls the passenger embeddings, and then averages these embeddings to generate the audience embedding.
We use the cosine score of a user and the audience embedding to identify the audiences the user belongs to. Hence, it’s sufficient to store only the audience embedding and score threshold. Additionally, a global target-all-pax Audience list is stored to return these audiences for each online request.
Serving lookalike audiences
The online audience service is also tasked with returning all the audiences to which the current user belongs. This is achieved by utilising the cosine score of the user embedding and audience embeddings, and filtering out all audiences that surpass the audience thresholds.
To adhere to latency requirements, we avoid querying any external feature stores like Redis and instead, store all the embeddings in memory. However, the embeddings of all users are approximately 20 GB, which could affect model loading. Therefore, we devised an embedding compression method based on hash tricks inspired by Bloom Filter.
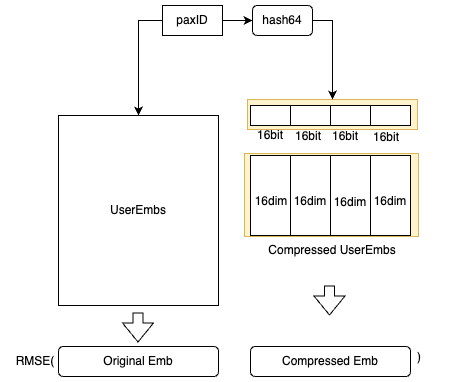
- We utilise hash functions to obtain the hash64 value of the paxID, which is then segmented into four 16-bit values. Each 16-bit value corresponds to a 16-dimensional embedding block, and the compressed embedding is the concatenation of these four 16-dimensional embeddings.
- For each
paxID, we have both the original user embedding and the compressed user embedding. The compressed user embeddings are learned by minimising the Mean Square Error loss. - We can balance the storage cost and the accuracy by altering the number of hash functions used.
Impact
- Users can see advertisements targeting a new audience within 15 mins after the advertiser creates a campaign.
- This new system doubled the impressions and clicks, while also improving the CTR, conversion rate, and return on investment.
- Costs for generating lookalike audiences decreased by 98%.
Learnings/Conclusion
To evaluate the effectiveness of our new scalable system besides addressing these issues, we conducted an A/B test to compare it with the earlier system. The results revealed that this new system effectively doubled the number of impressions and clicks while also enhancing the CTR, conversion rate, and return on investment.
Over the years, we have amassed over billions of user actions, which have been instrumental in training the model and creating a comprehensive representation of user interests in the form of embeddings.
What’s next?
While this scalable system has proved its effectiveness and demonstrated impressive results in CTR, conversion rate, and return on investment, there is always room for improvement.
In the next phase, we plan to explore more advanced algorithms, refine our feature engineering process, and conduct more extensive hyperparameter tuning. Additionally, we will continue to monitor the system’s performance and make necessary adjustments to ensure it remains robust and effective in serving our advertisers’ needs.
References
Grab is the leading superapp platform in Southeast Asia, providing everyday services that matter to consumers. More than just a ride-hailing and food delivery app, Grab offers a wide range of on-demand services in the region, including mobility, food, package and grocery delivery services, mobile payments, and financial services across 428 cities in eight countries.
Powered by technology and driven by heart, our mission is to drive Southeast Asia forward by creating economic empowerment for everyone. If this mission speaks to you, join our team today!



